A Genome-Wide CROP-Seq CRISPRi Screen for Factors of TCR Signaling
At Myllia, the Perturb-seq (CROP-seq) workflow has been adapted to enable genome-scale CRISPRi (CRISPR interference) screens in Jurkat cells at single-cell resolution. The first-of-its-kind genome-scale CRISPRi screen was conducted to verify factors involved in TCR signaling pathways.
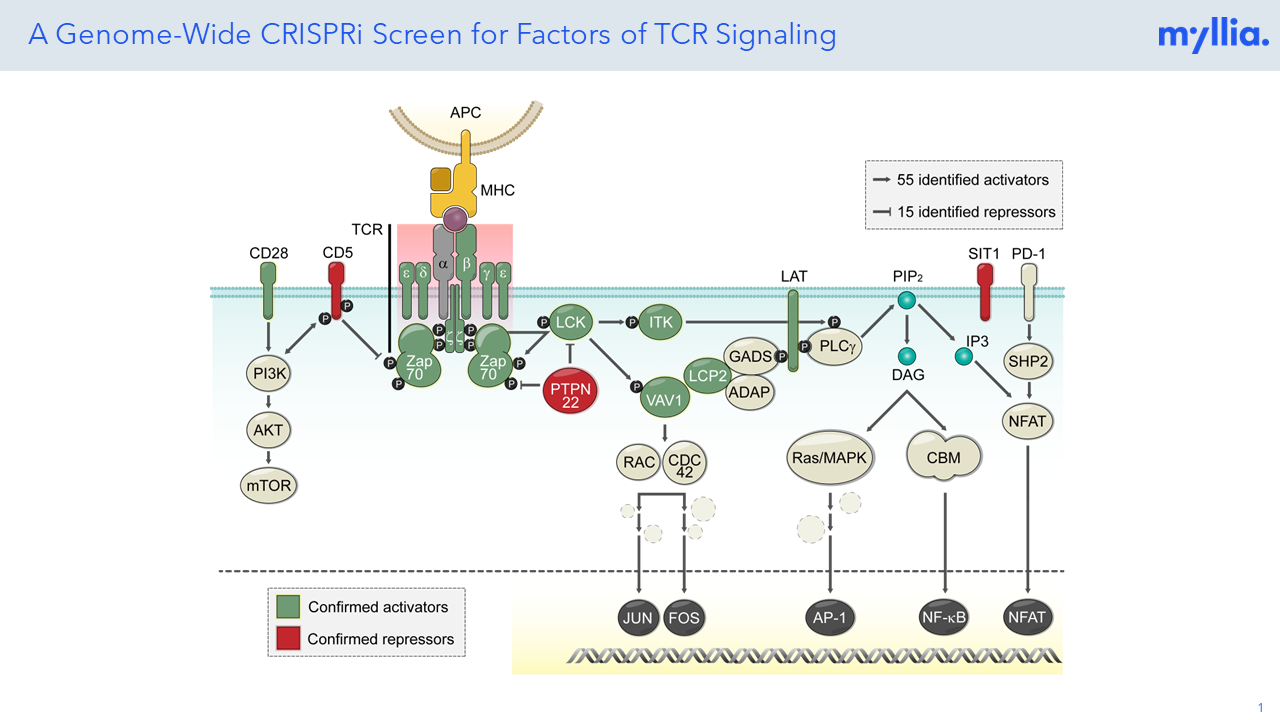
T-cell receptor signaling plays a crucial role in the immune response, initiating a cascade of signaling events that regulate T-cell activation, differentiation, and effector functions. Unravelling these T cell-intrinsic molecular factors could potentially unlock new therapeutic targets and strategies for modulating T cell responses in various immune-related disorders.
The Screen
At Myllia, the Perturb-seq (CROP-seq) workflow has been adapted to enable genome-scale CRISPRi (CRISPR interference) screens in Jurkat cells at single-cell resolution. The first-of-its-kind genome-scale CRISPRi screen was conducted to verify factors involved in TCR signaling pathways. In more detail, a guide RNA library targeting 18,595 human genes was utilized for CRISPR-based gene knockdowns in Jurkat cells expressing the dCas9-KRAB fusion endonuclease. In total, one million Jurkat cells were processed for single-cell RNA sequencing allowing transcriptomic readouts of a final list of 374 marker genes involved in TCR signaling.
Results & Conclusion
The bioinformatic analysis confirmed more than 70 known activators and repressors of TCR signaling cascades, hence showcasing the potential of Perturb-seq (CROP-seq) screens to support translational research. The set of 70 genes affected T cell activation, partitioning to 55 activators (whose
knockout led to diminished signaling) and 15 inhibitors (whose knockout led to enhanced signaling).
Submit your credentials and explore our capabilities and functional read-outs!
