A CROP-Seq Screen for Modulators of Th2 Cell Polarization
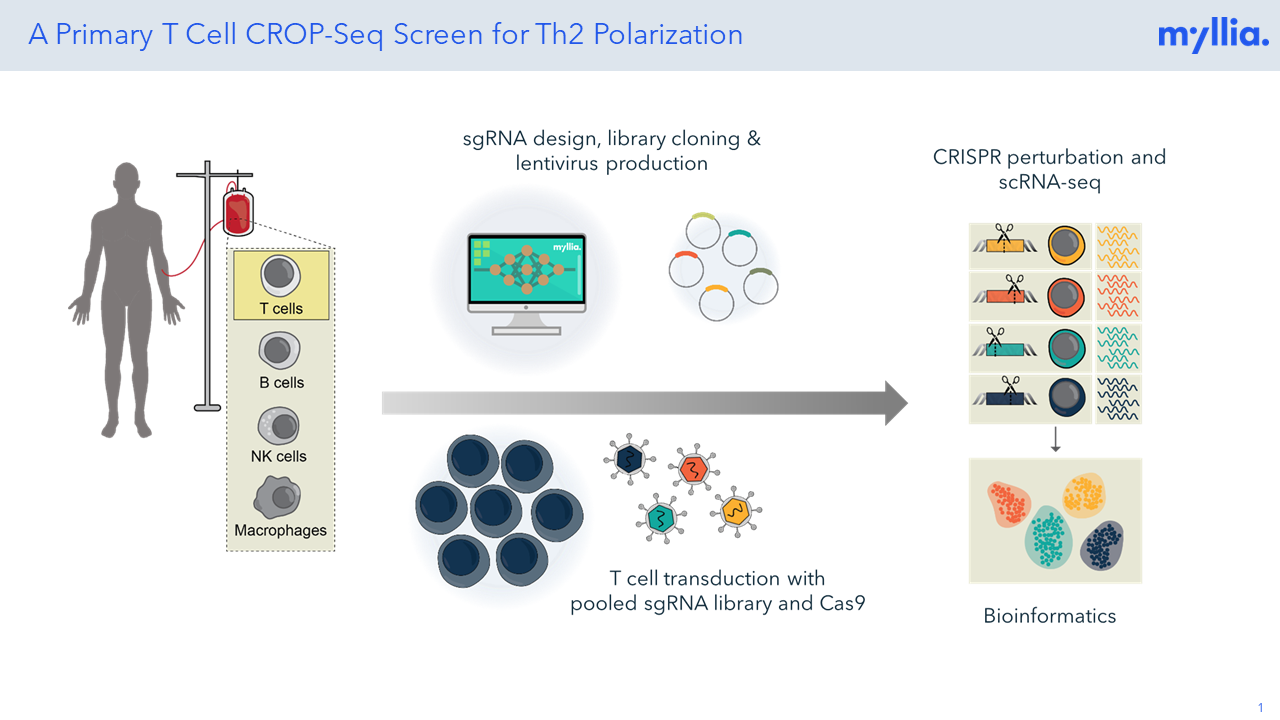
In a CROP-Seq experiment with CD4+ T cells, Th2-skewed cells were studied using a sgRNA library targeting 102 genes with a targeted read-out of 300 mRNAs.
T helper 2 (Th2) cell differentiation plays a critical role in regulating allergic responses, defense against parasites, and immune homeostasis. However, the interplay of cytokines, transcription factors, and epigenetic modifications in driving T cell fates is still not fully understood. Recently, functional genomics and CRISPR screening have emerged as powerful tools to unravel the factors involved in T helper cell differentiation aiming to support the development of cell-based therapies in conditions like allergies and autoimmune diseases.
The Screen
At Myllia, CRISPR screening enables the systematic perturbation of genes to determine their functional impact on T cell differentiation. This approach allows for the identification of novel gene regulatory networks involved in T helper cell differentiation. In a CROP-Seq experiment with CD4+ T cells, Th2-skewed cells were studied using a sgRNA library targeting 102 genes with a targeted read-out of 300 mRNAs.
Results & Conclusions
The knockout of IL4R and HDAC4 genes resulted in depletion in differentiated Th2 cells, suggesting their importance in Th2 cell differentiation. On the other hand, the knockout of IL2RA and NFATC2 was found to be enriched in differentiated Th2 cells, indicating their potential role in promoting Th2 cell differentiation. Leveraging our proprietary know-how on T cell subsets and transcriptomic markers, we can improve the assessment of T cell plasticity at large scale enhancing the potential of CRISPR screens in primary T cells.
Submit your credentials and explore the Th2 CRISPR screen in more detail!
